22 Coronavirus myths and facts – what is the truth about Covid-19?
What are the most important Coronavirus myths and facts? What is true and what is false? What are the myths and certain truths? Are face masks a reliable protective measure? The climate influences the development of the virus? Is vodka a good hand disinfectant? Are the elderly the only ones affected by the virus? Can animals spread the disease? Can covid-19 be transmitted to humans through an insect bite? Are there foods and remedies that protect from coronavirus? We will bust 22 myths about Covid-19 in the article!
In addition to infecting thousands of people worldwide, Covid -19 coronavirus has been a subject of numerous fake news and disinformation. Faced with the fear and stress caused by the pandemic, many people begin to believe and share false information. This is one of the main reasons why experts advise filtering your news sources and only trust officials. Credible and up-to-date news and pandemic news can usually be found on the World Health Organization website.
Prevention measures to limit the spread of coronavirus disease are taken all over the world and we have paid special attention on the importance on 20 second hand washing, cleaning and disinfecting surfaces in the house with disinfectant products, and social distance and isolation. However, misinformation circulates social media and questionable sources, so
Coronavirus myths and facts – Knowledge is power
Myths, lies, and conspiracy theories about the coronavirus spread even faster than the virus itself. It is understandable that people are worried but we all need to keep our common sense especially when we are in the middle of a pandemic. Here is what you need to know about the myths surrounding COVID-19 and what the experts are saying.
Myth 1 – Covid-19 is a biological weapon created in a laboratory
Some experts suspect that SARS-CoV-2 jumped from pangolins (a wild animal sold in China for its meat) to humans. Another rumor is that the virus passed to humans from bats. Another statement circulating social media is that the outbreak began because people ate bat soup. Despite the fact that scientists are confident that the virus started in animals, it is naïve to believe it came from a soup. You should treat such news as rumors.
Myth 2 – Hold your breath for 10 seconds
The first myth is that if you can hold your breath for 10 seconds, you do not have coronavirus infection. This is not true. The idea behind this myth is that when people get infected with coronavirus, 50% of their lungs suffer from pulmonary fibrosis. The truth is that it is possible that coronavirus causes fibrosis but holding your breath is not a reliable test that will show you if you have any lung damage. If you have any breathing difficulties, you should call your doctor.
Myth 3 – Coronavirus is like any other flu
Although the symptoms are similar, the coronavirus incubation period is longer, which increases the risk of infection. SARS-CoV-2 causes a disease that has flu-like symptoms, such as pain, fever and cough. Both flu and coronavirus can lead to pneumonia. Flu vaccine is completely useless against the coronavirus. There is currently no treatment for covid-19.
Myth 4 – Drinking water
Another widespread coronavirus myth is that drinking water can wash down the Covid virus in your mouth. This is false. Drinking water every 15 minutes will not help you against coronavirus infection. Neither will gargling with warm water and salt or vinegar or flushing your nose with saline spray. According to WHO (World Health Organization) there’s no evidence that drinking water can protect you from getting the coronavirus. However, being well hydrated is a good idea whether you’re sick or not.
Myth 5 – Face masks are the most effective protection against coronavirus
Disposable face masks are unlikely to provide protection because they do not fit properly and droplets can still enter the mouth and nose. If you have symptoms of coronavirus or you are caring for someone who may be infected, wearing a mask is essential. Some doctors, however, claim that the mask tends to lower alertness and provide a “false sense of security” to the wearer. It must be adapted to the size and shape of the face and must be well positioned: the padded side of the nose strip must be placed on the bump of the nose to protect it properly. Whether conventional or homemade, its lifespan is only 3 hours. At the end of this time, the risk of contamination increases considerably.
Myth 6 – There are remedies for coronavirus
Faced with the lack of treatment for the coronavirus and the speed of its progression, it is psychosis that sets in, while leaving room for many rumors about so-called miracle home remedies that would help fighting it. And if some of them can possibly relieve certain symptoms like cough, the majority of those prove to be absolutely ineffective. The myth that gargling bleach will protect you from coronavirus is actually dangerous. Bleach is corrosive and can cause serious damage!
Excessive garlic consumption will not protect you from covid-19. While garlic may slow down the growth of some bacteria, COVID-19 is caused by a virus and garlic has no effect whatsoever. The same is valid for antibiotics. They can kill bacteria, but they do not kill viruses.
Vitamin C does not protect you from coronavirus. Despite the fact that many people believe that vitamin C will beat Covid infection, at the moment there is no solid proof that it will help you in the fight against the deadly coronavirus.
Another misconception is that chlorine or alcohol on skin kills viruses in the body. These products can be very dangerous and harmful, especially if they enter the eyes or mouth. 60-70% alcohol and bleach can be used to disinfect surfaces but should not be used on skin and certainly cannot kill viruses in the body.
Myth 7 – Pneumonia and flu vaccines protect you
It is essential to understand that at the moment there is no coronavirus vaccine and according to WHO, it is false for people to say that pneumonia vaccines will protect you against it. Researchers are trying to develop a vaccine against 2019-nCoV, and WHO is supporting their efforts but it is unlikely that a vaccine will be available soon.
Myth 8 – Covid-19 virus doesn’t survive in warm weather
A popular myth about coronavirus is that it cannot survive in hot climate. According to the WHO, however, the coronavirus can be transmitted in all regions of the world, even in hot climates. The truth is that the climate does not influence the development of the virus and it can grow even in warmer, more humid areas. Snow and freezing temperatures cannot kill the virus either.
Myth 9 – Taking a hot bath will prevent me from getting coronavirus
This is not true. A hot bath is a great way to relax and ease stress but will not protect you from the Covid-19 virus. Why? Because the normal body temperature remains around 36.5°C to 37°C (97.7 °F to 98.6 °F) regardless of the temperature of the water in the bathtub or shower.
Myth 10 – Receiving a package from China is dangerous
Another question that caused an avalanche of question marks and comments on the Web is “Is it safe to receive a package or a letter from China? According to the WHO, this is also misinformation and people who receive parcels from China are not at risk. Generally, SARS-COV-2 can indeed survive outside the human body, but its lifespan on different surfaces like wood, stainless steel, plastic, steel, copper, etc., is not unlimited. This means that by the time your package or letter arrives at your post box, the danger will be gone.
Myth 11 – Using cleansing gel is just as effective as washing your hands
When hand disinfectants became scarce or totally disappeared in stores, people were looking for other ways to protect themselves. The good old fashioned method of washing hands with water and soap goes a long way in killing germs and viruses. According to public health experts, the disinfectant liquid based on 70% alcohol is only a temporary cleaning solution to be used only when you do not have access to water or soap.
Myth 12 – Insects transmit coronavirus disease
No, insects, especially mosquitoes, do not transmit the coronavirus and the reason is pretty obvious. Due to the fact that covid-19 is a respiratory transmissible virus, mosquito bites pose no risk of contamination.
Myth 13 – Pets spread coronavirus
No, dogs and cats do not transmit the coronavirus. Covid-19 is a virus that is currently spread from human to human.
Myth 14 – Only elderly people are at risk
Another misconception about coronavirus is that it only affects the elderly. Although this group is more “fragile”, like other coronaviruses, SARS-COV-2 can infect people of any age especially people suffering from a preexisting disease, such as diabetes, asthma, transplant, cancer.
Myth 15 – Children cannot catch coronavirus
Like we said above, SARS-COV-2 can infect people of any age, including children. Children are not immune but their symptoms tend to be less severe.
Myth 16 – Everyone with COVID-19 dies
This is untrue. Coronavirus is fatal for a small percentage of people. According to WHO around 80% of people will experience a relatively mild form of the disease, which will not require hospital treatment. The mild Covid-19 symptoms may include fever, cough, sore throat, tiredness, and shortness of breath. Fortunately, most of infected people around the world have already recovered and are considered cured.
Myth 17 – I don’t have coronavirus because I don’t have symptoms
Yes, it is entirely possible to be asymptomatic and to be a carrier of the virus. In this case, precautionary measures and social isolation become more than essential, in order to limit the risks of spreading the virus as much as possible. According to the WHO, the risk of being infected by a person carrying the Covid-19 virus, who has no symptoms, remains very low.
Myth 18 – Healed person is immune
After healing, each patient develops antibodies against the virus. As for the coronavirus, this is not necessarily the case. Several people were diagnosed positive more than once.
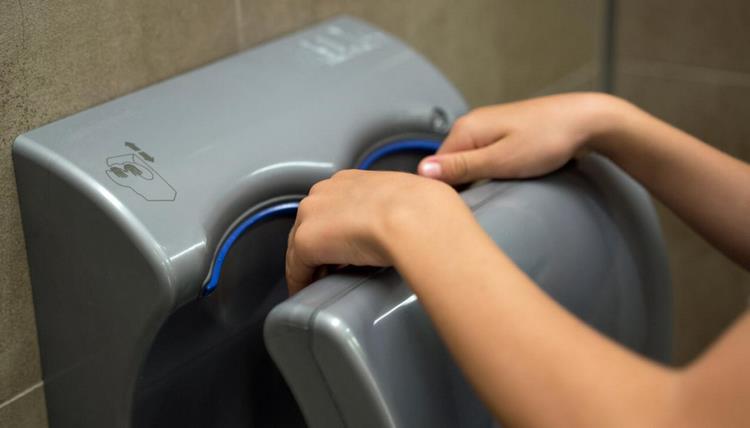
Myth 19 – Hand dryers kill coronavirus
Totally false! Hand dryers do not kill coronavirus. The best way to protect yourself and others is washing your hands with warm water and soap or using alcohol-based hand sanitizer if soap and water are not available.
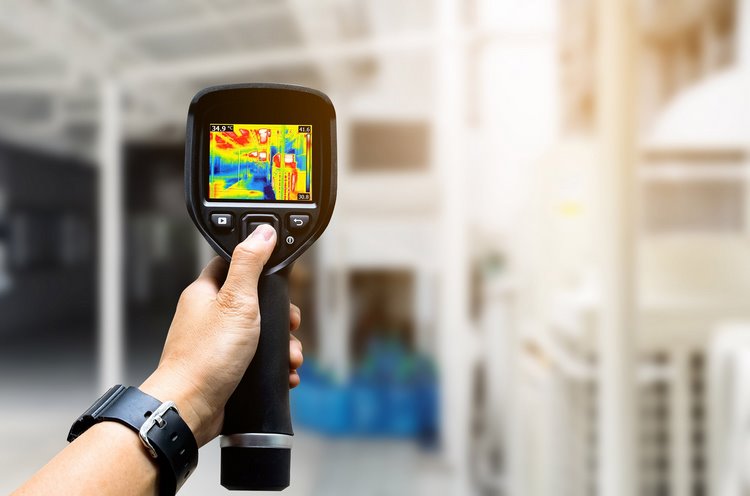
Myth 20 – Thermal scanners can diagnose coronavirus
No, they cannot. Thermal scanners can detect whether someone has a fever. However, fever can be caused by many other conditions. Having in mind the fact that symptoms of COVID-19 can appear 2–10 days after infection, an infected person could have a normal temperature before a fever begins.
Myth 21 – You can catch coronavirus from eating Chinese food
No, you cannot.
Myth 22 – Coronavirus is the deadliest virus known to man
No, it is not. Obviously, SARS-CoV-2 is way more serious than influenza but it is not the deadliest virus known to man. Ebola virus, for example, has higher mortality rate.
Hopefully, this detailed information about coronavirus myths and facts is useful to you. Please, bear in mind that it is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as health or medical advice. If you have any questions about an illness or current health issues, consult a doctor or other qualified healthcare provider.