Septic tank systems come in different designs and choosing the right one for your home requires some knowledge about septic tanks types, materials, advantages and disadvantages of the different materials, how to choose the size of the tank, etc. In addition, you need to keep in mind and plan the way of transport, the installation care and maintenance of your system. As you can see – there are many factors to consider and we shall give you some useful information for the different types of systems and the way they function.
The choice of a septic tank system is usually determined by the way it is going to be used. The size will depend on how big your family is, whether you choose a system for your holiday house which is not regularly occupied or for your permanent home, the number of bathrooms, etc. The type will also depend on the land lot and the location – for example, on a small lot you cannot install a huge construction or if you need a septic system for a mountain house you need to keep in mind the eventual problems with installation, rainfall, underground water, etc. It is best if you consult with a specialist who will be able to advise you what is best for your particular needs.
Septic tank system – types of tanks and principle of functioning
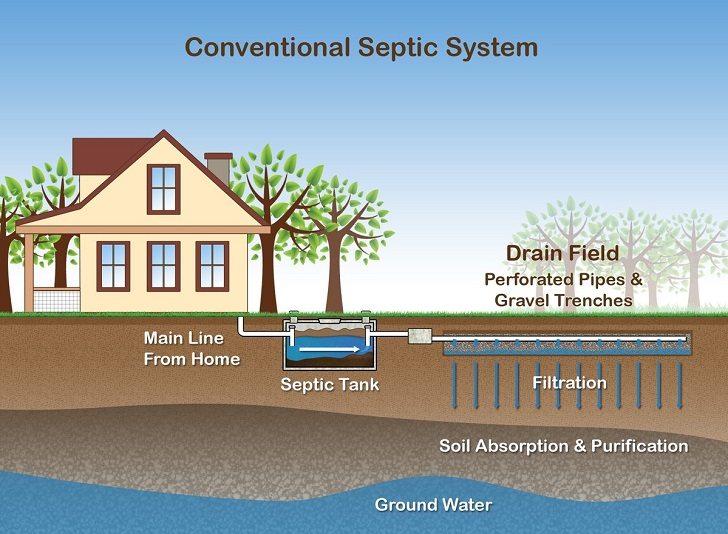
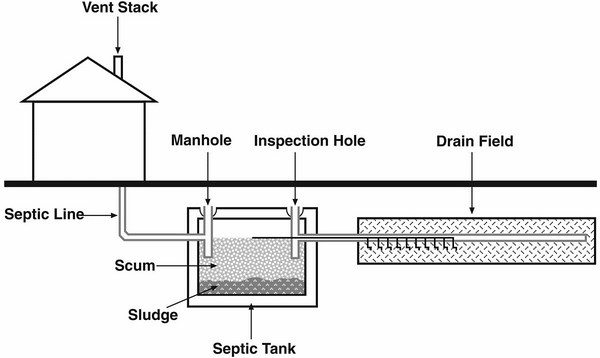
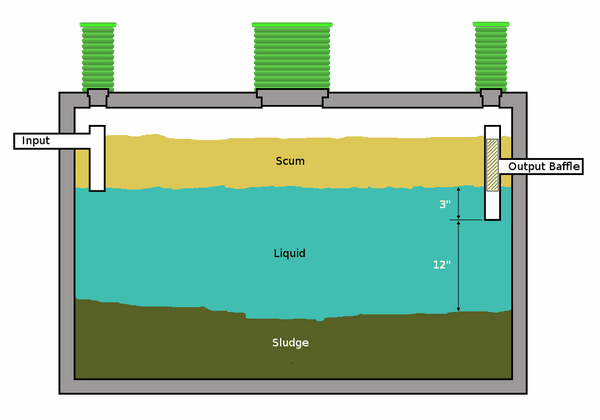
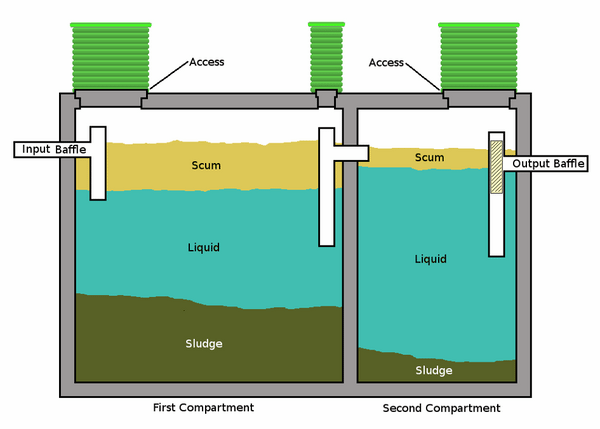
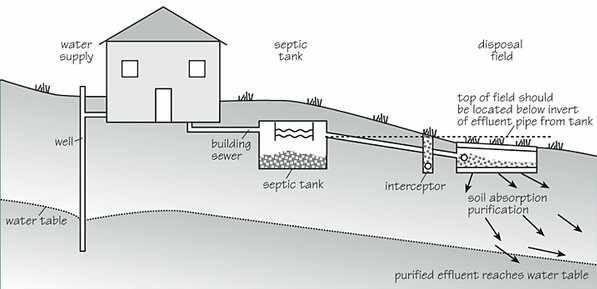
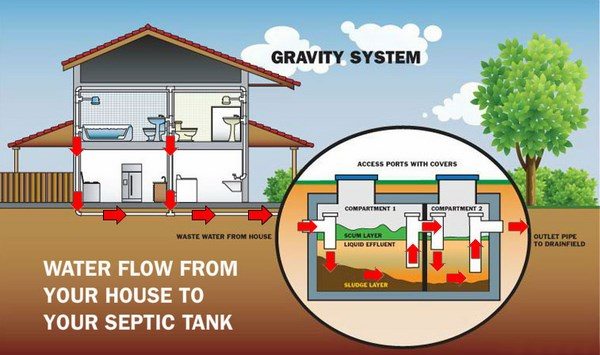
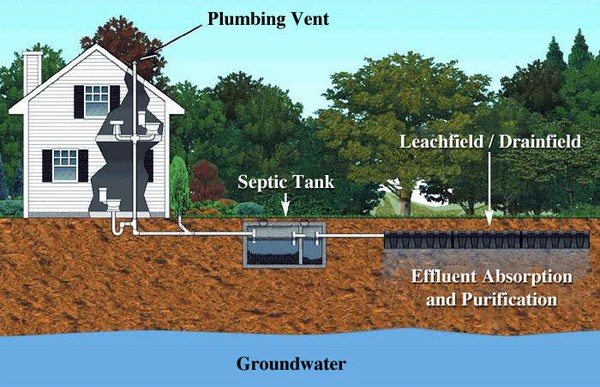
Which septic tank system is the best? There is not one answer to this question – one system will work for you while other homeowners will see more advantages in another type. Generally all septic tank systems consist of two main elements – a tank and a drain field. The tank contains all the wastewater of a household and solid components and water are separated in the tank. Wastewater liquid is treated (effluent) and goes to a drain filed where it is absorbed by the soil. No matter what type of system you choose the main functions of any septic tank are to provide space where the fats and solids from the wastewater are separated from the liquids, to break down the solids through a biochemical process and provide storage for the sludge until the tank is pumped. Every tank contains three layers – a bottom layer of solids, called sludge, a layer of clear liquid waste (effluent) also called a clear zone and a layer of fats (scum), which is floating on the surface of the liquid waste.
Septic tanks are made of different materials – steel, concrete, pre-cast concrete, plastic and fiberglass. Each material has its own pros and cons, but concrete and plastic tanks are the most popular choices. However, beside the material, tanks differ in construction.
You can choose between a single chambered tank or multi-chambered tanks. Single compartment tanks typically have one main lid and two smaller lids at the two ends. Double compartment tanks offer the advantage an additional space and allow the solids to settle more effectively from the effluent before it travels to the drain field. However, this does not mean that they do not need to be pumped as you risk an overflow of solids to the drain field.
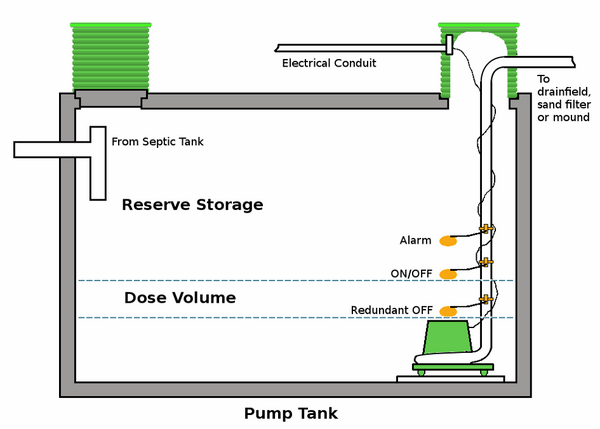
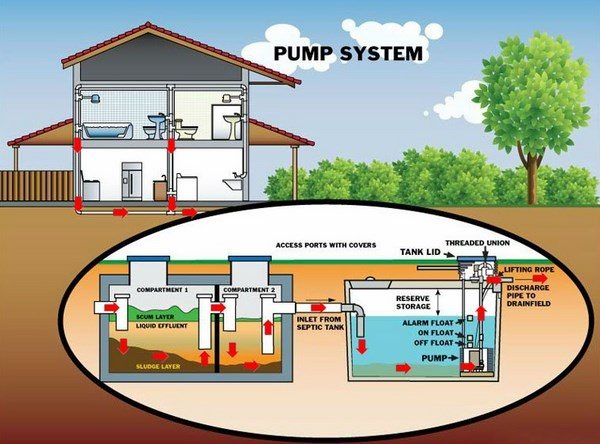
Pump tanks are equipped with a sewage effluent pump, control floats, and a high water alarm. Their principle of functioning is based on setting the control floats to activate when the effluent reaches a certain level and the pump sends it to the drain field. The function of the alarm box is to give a signal if there is a problem with the components of the tank.
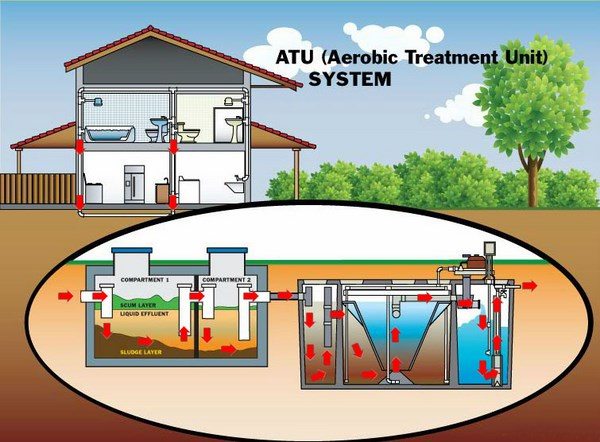
Aerobic tanks are an alternative to the conventional tanks and contain an Aerobic Treatment Unit which consists of a compartment holding the solids, an aerobic chamber where the effluent is treated, and a clarifying compartment. Aerobic septic tanks are a good choice when you have a small lot or poor soil drainage.
Septic tank systems – choosing the type of system for your home
As we mentioned above there are two main types of septic tanks systems – conventional and alternative and the choice will depend on your individual needs, site, soil conditions, etc. Conventional septic systems include Gravity systems and Pressure distribution systems.
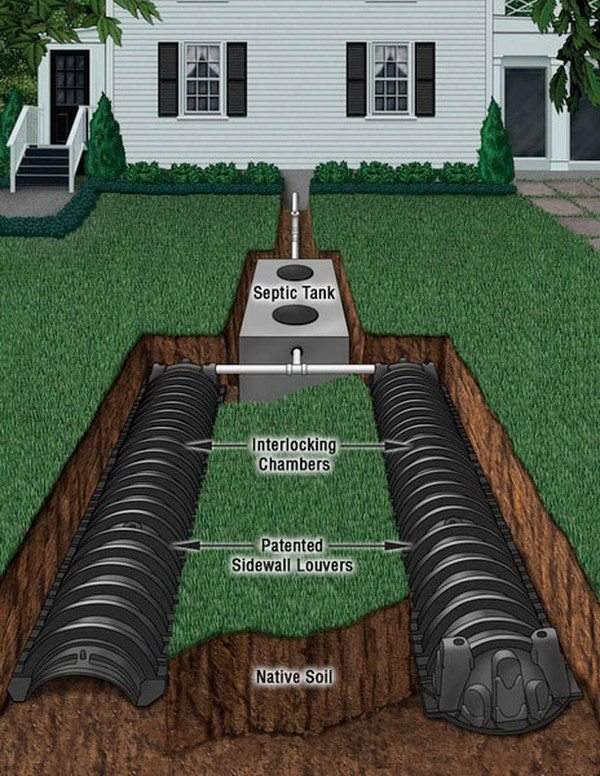
Gravity systems include three elements – a septic tank, a drain field and a level of soil under the drain field. As the name suggests, these systems use gravity to move effluent through the septic tank and into the drain field. This conventional septic system also contains a layer of gravel on the drain field and perforated pipes lie on the gravel. When the effluent enters the pipes in the drain field it is filtered through the gravel. The bacteria in the soil below the gravel will consume any organic components in the wastewater. Usually, gravity septic systems have a distribution box which distributes wastewater into the pipes in the drain field.
Pressure distribution septic systems use a pump chamber where wastewater from the septic tank is collected and the pump distributes the effluent into the pipes of the drain field. Typically the pump is on the floor of the pump chamber and the floats control and turn on and off the pump when the wastewater reaches the preset level. A high-water alarm float will indicate when the levels of wastewater are too high. Some pump systems may use a timer instead of float control.
Gravel or stone septic systems have some drawbacks which you need to keep into consideration. The gravel limits the ability of effluent to reach the soil and depending on the size of the gravel there may be a blockage. Typically, the gravel level consists of washed gravel, but it is impossible to avoid a certain amount of fine particles and they are the reason for the reduced filtration and potential drain filed overloads.
Alternative septic tanks systems include aerobic septic systems, sand filter systems, mound septic system, surface distribution system, evaporation system, etc. Here are the basic features of these systems.
Evaporation (Evapotraspiration systems) septic tank systems are based on s the natural evaporation of wastewater through a sand barrier level and a simultaneous transpiration of water through the leaves of plants and grasses which are planted above the drain field area. Obviously these systems are most effective in summer periods when the hours of sunlight provide the most effective wastewater processing and are most suitable for summer homes.
Aerobic septic tank systems provide an environment rich in oxygen to organisms and bacteria that reduce the organic part of the waste. One particular feature of aerobic septic systems is that they require oxygen to function and the ATU (aerobic treatment units) are equipped with a mechanism which injects and circulates air inside the aerobic tank. The main advantages of aerobic septic systems include a high level of wastewater treatment, these systems aid the protection of water resources and are a great alternative for areas where you cannot install a conventional septic system.
A surface distribution system (sprinklers) strongly resembles a normal lawn irrigation system and functions of the same principle. Treated wastewater is distributed via sprinklers to the ground surface. These systems require the most efficient treatment of wastewater as it actually may contact with the home occupants or family pets so you need to pay special attention to maintenance and regularly check the septic system to prevent any potential problems.
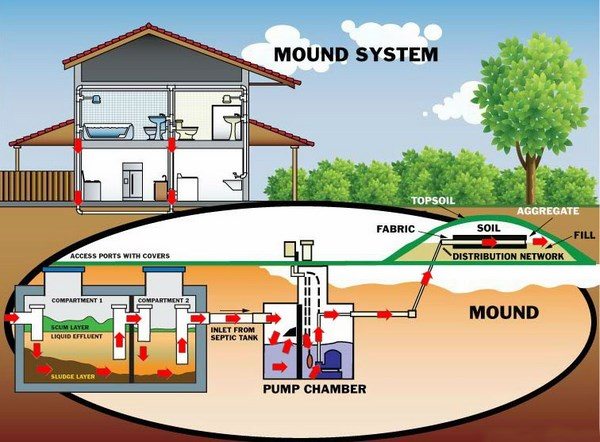
Mound septic tank systems are suitable for areas with minimal soil. Their main feature of this type of septic system is that the drain field is above the ground level. After the pipes are installed on the ground (no digging of trenches is involved) they are covered with soil and grass and the wastewater drips into the soil through a level of gravel and special sand fill.
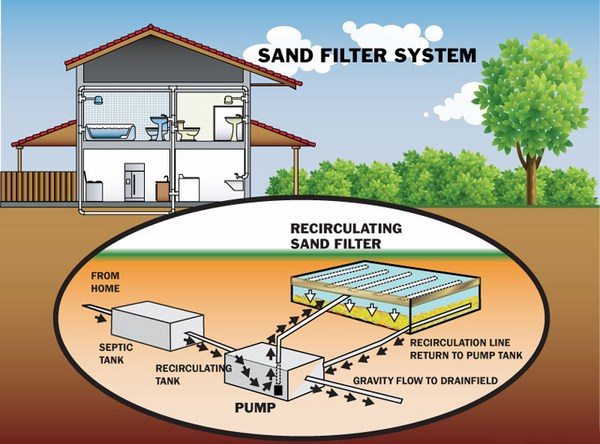
Sand filter septic systems come in different designs but generally they consist of a sand filtering system which is placed in a watertight box (PVC-lined or concrete box) built into the soil. Pipes are placed on top of the sand in beds that could be filled with gravel. It is the sand layer that treats the effluent which is distributed in the pumps with the help of a pump chamber and after that is collected to the bottom of the box. Once collected, the processed water is pumped to the drain field and is more easily absorbed in the soil.
Alternative systems also include drip emitters system, systems constructed with different layers of sand and gravel, textile material, etc.